⫹⫺ Cognitive Biases 101
For the Creators, Makers & Doers - CMMN WLTH
Hello my friends,
While researching for CMMN WLTH I inadvertently read a lot about cognitive biases.
Cognitive biases are errors of thinking commonly caused by the brain’s attempt to oversimplify information.
Understanding them will help you make better everyday decisions.
Here are the 10 most useful, explained with examples ↓
1/ Dunning-Kruger
You think you know more than you actually do.
The Dunning-Kruger effect occurs when a person’s lack of knowledge and skills in a certain area cause them to overestimate their own competence.
2/ Anchoring
You rely too heavily on the first piece of information you receive on a topic.
This one is often used in salary negotiation.
HR uses a low number to anchor the conversation down.
What should you do?
Propose a high anchor to pull the conversation back up.
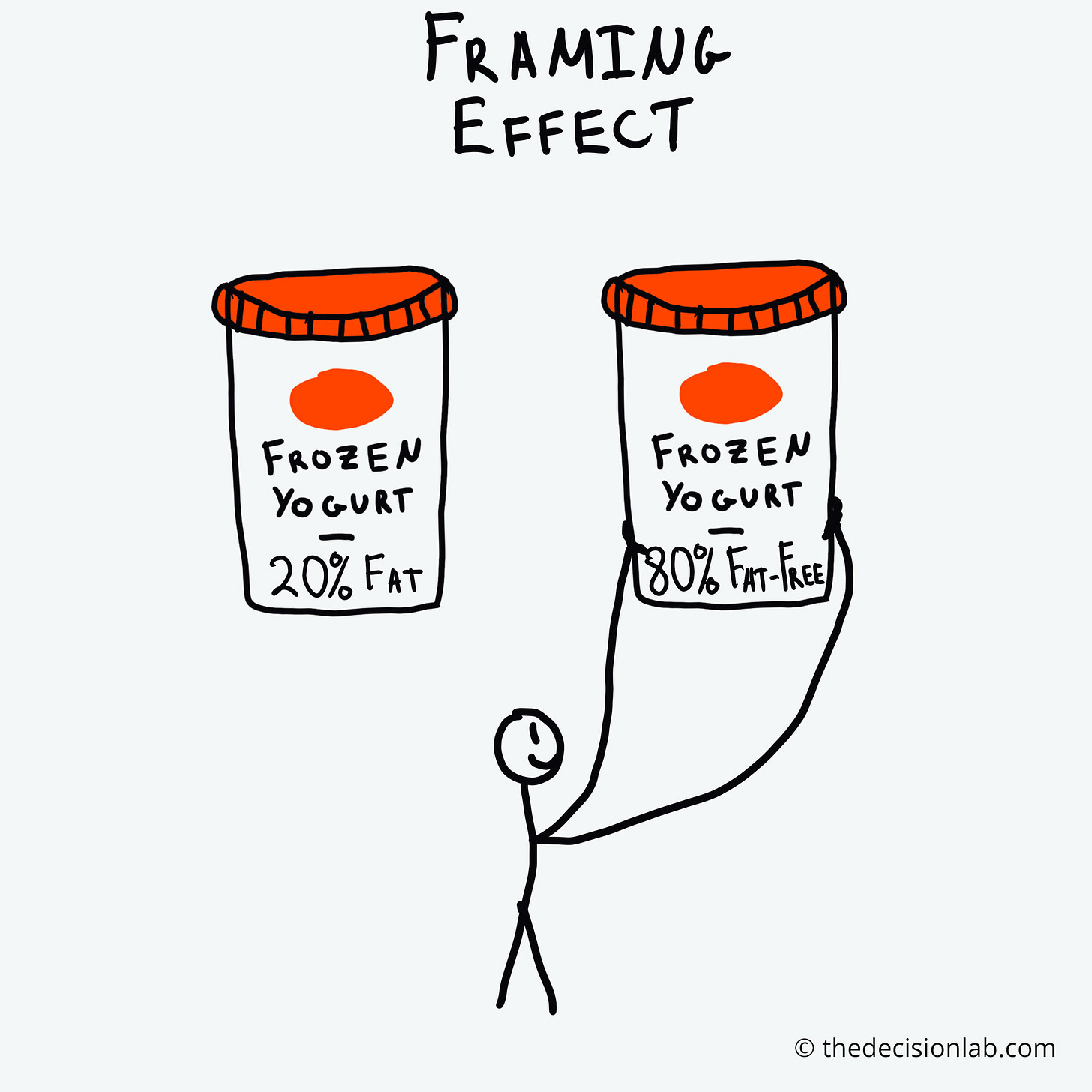
3/ Framing
Our decisions are influenced by how information is presented.
Equivalent information can be more or less attractive depending on how it is presented.
Which one sounds better? ↓
4/ Sunken Cost Fallacy
You’ve put effort and money into a project and although following through doesn’t make sense you just can’t let it fail.
Exhibit A ↓
5/ Confirmation Bias
The tendency to search for, interpret or recall information in a way that confirms or supports your prior beliefs or values.
One of the most common in daily life. Overcome it by looking critically at your initial conclusion.
6/ Prospect Theory
You value gains and losses disproportionally.
Presented with:
An investment opportunity that has an average return of 10% for the last three years.
OR
One with above-average returns over the last decade, but has been in decline for the last three years.
Prospect Theory states that although the two are the same opportunity the investor will go with the first option.
7/ Apophenia
A tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things.
When you go to the casino and think you see patterns in random information.
(Winning two hands in a row doesn’t mean you can count cards…sorry)
8/ Familiarity Principle
When you develop a preference for something based purely on how familiar you are with it.
Also known as the mere-exposure effect.
9/ Cognitive Dissonance
The uncomfortable feeling you get when your feelings don’t align with your actions.
You love the environment but you still throw plastic bags in the trash.
10/ Present Bias
The inclination to prefer a smaller reward in the short term than a larger later reward.
Really, who can resist one marshmallow now for two later, not this guy ↓
Sharing this newsletter helps it grow.
Your feedback helps make it great.